ב-Espresso יש מנגנונים שאפשר לגלול או לבצע פעולות על פריט מסוים בשביל שני פריטים סוגי רשימות: תצוגות מתאמים ותצוגות של מיחזור.
כשמדובר ברשימות, במיוחד אלה שנוצרו באמצעות RecyclerView או
AdapterView, יכול להיות שהתצוגה שמעניינת אותך לא תוצג אפילו
במסך מכיוון שרק מספר קטן של ילדים מוצג
לממוחזר תוך כדי הגלילה. במקרה הזה אי אפשר להשתמש ב-method scrollTo()
כי הוא מחייב תצוגה קיימת.
אינטראקציה עם פריטים ברשימת התצוגות של המתאמים
במקום להשתמש בשיטה onView(), מתחילים את החיפוש עם onData()
לספק התאמה לנתונים שמגבים את התצוגה שאליה רוצים להתאים.
המערכת של Espresso תבצע את כל העבודה הבאה כדי למצוא את השורה באובייקט Adapter,
הפיכת הפריט לגלוי באזור התצוגה.
התאמת נתונים באמצעות כלי להתאמה אישית של תצוגות מפורטות
הפעילות שבהמשך מכילה ListView, שמגובה על ידי SimpleAdapter
שמכילה את הנתונים של כל שורה באובייקט Map<String, Object>.
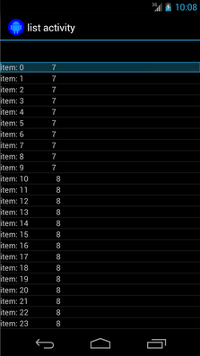
בכל מפה יש שתי רשומות: מפתח "STR" שמכיל מחרוזת, כגון
"item: x", ומפתח "LEN" שמכיל Integer, שמייצג את
אורך התוכן. לדוגמה:
{"STR" : "item: 0", "LEN": 7}
הקוד לקליק על השורה עם "item: 50" נראה כך:
Kotlin
onData(allOf(`is`(instanceOf(Map::class.java)), hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), `is`("item: 50")))).perform(click())
Java
onData(allOf(is(instanceOf(Map.class)), hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), is("item: 50")))) .perform(click());
לתשומת ליבכם: Espresso גולל ברשימה באופן אוטומטי לפי הצורך.
בואו נפרק את Matcher<Object> שבתוך onData().
השיטה is(instanceOf(Map.class)) מצמצמת את החיפוש לפריט כלשהו
AdapterView, שמגובה על ידי אובייקט Map.
במקרה שלנו, היבט זה של השאילתה תואם לכל שורה בתצוגת הרשימה, אך אתם רוצים ללחוץ ספציפית על פריט מסוים, לכן אנחנו מצמצמים את החיפוש עוד יותר עם:
Kotlin
hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), `is`("item: 50"))
Java
hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), is("item: 50"))
Matcher<String, Object> זה יתאים לכל מפה שמכילה רשומה עם
המפתח "STR" והערך "item: 50". בגלל שהקוד לחיפוש הוא
ואנחנו רוצים להשתמש בו שוב במיקומים אחרים,
תואם withItemContent למטרה הזו:
Kotlin
return object : BoundedMatcher<Object, Map>(Map::class.java) { override fun matchesSafely(map: Map): Boolean { return hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), itemTextMatcher).matches(map) } override fun describeTo(description: Description) { description.appendText("with item content: ") itemTextMatcher.describeTo(description) } }
Java
return new BoundedMatcher<Object, Map>(Map.class) { @Override public boolean matchesSafely(Map map) { return hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), itemTextMatcher).matches(map); } @Override public void describeTo(Description description) { description.appendText("with item content: "); itemTextMatcher.describeTo(description); } };
משתמשים ב-BoundedMatcher כבסיס כי כדי להתאים רק אובייקטים מסוג
Map. ביטול השיטה matchesSafely() והוספת ההתאמה שנמצאה
קודם, ומתאימים אותו ל-Matcher<String> שאפשר להעביר
ארגומנט. כך תהיה לך אפשרות להתקשר אל withItemContent(equalTo("foo")). לקוד
מקוצר, אפשר ליצור התאמה נוספת שכבר קוראת לequalTo() וגם
מקבל אובייקט String:
Kotlin
fun withItemContent(expectedText: String): Matcher<Object> { checkNotNull(expectedText) return withItemContent(equalTo(expectedText)) }
Java
public static Matcher<Object> withItemContent(String expectedText) { checkNotNull(expectedText); return withItemContent(equalTo(expectedText)); }
עכשיו הקוד ללחיצה על הפריט הוא פשוט:
Kotlin
onData(withItemContent("item: 50")).perform(click())
Java
onData(withItemContent("item: 50")).perform(click());
כדי לקבל את הקוד המלא של הבדיקה הזו, אפשר לעיין בשיטה testClickOnItem50().
במסגרת
AdapterViewTest
כיתה
LongListMatchers המותאם אישית הזה
תואם ב-GitHub.
התאמה לתצוגת צאצא ספציפית
הדוגמה שלמעלה גורמת לקליק באמצע השורה כולה של ListView.
אבל מה אם אנחנו רוצים לנתח צאצא ספציפי של השורה? לדוגמה, אנחנו
רוצה ללחוץ על העמודה השנייה בשורה של LongListActivity,
שמציג את ה-String.length של התוכן בעמודה הראשונה:

פשוט צריך להוסיף מפרט onChildView() להטמעה של
DataInteraction:
Kotlin
onData(withItemContent("item: 60")) .onChildView(withId(R.id.item_size)) .perform(click())
Java
onData(withItemContent("item: 60")) .onChildView(withId(R.id.item_size)) .perform(click());
אינטראקציה עם פריטים ברשימת התצוגה של מיחזור
RecyclerView אובייקטים פועלים באופן שונה מ-AdapterView אובייקטים, כך
לא ניתן להשתמש באפליקציה onData() כדי לקיים איתם אינטראקציה.
כדי לבצע אינטראקציה עם RecyclerViews דרך Espresso, אפשר להשתמש
חבילת espresso-contrib, עם אוסף של
RecyclerViewActions
שיכול לשמש כדי לגלול למיקומים או כדי לבצע פעולות על פריטים:
scrollTo()– גלילה לתצוגה התואמת, אם היא קיימת.scrollToHolder()– גלילה לבעלים של התצוגה המפורטת, אם קיים.scrollToPosition()– גלילה למיקום ספציפי.actionOnHolderItem()– מבצעת פעולת צפייה בבעל צפייה תואם.actionOnItem()– מבצעת פעולת צפייה בתצוגה תואמת.actionOnItemAtPosition()- מבצעת ViewAction בצפייה במיקום ספציפי.
בקטעי הקוד הבאים אפשר למצוא כמה דוגמאות RecyclerViewSample דוגמה:
Kotlin
@Test(expected = PerformException::class) fun itemWithText_doesNotExist() { // Attempt to scroll to an item that contains the special text. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform( // scrollTo will fail the test if no item matches. RecyclerViewActions.scrollTo( hasDescendant(withText("not in the list")) ) ) }
Java
@Test(expected = PerformException.class) public void itemWithText_doesNotExist() { // Attempt to scroll to an item that contains the special text. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) // scrollTo will fail the test if no item matches. .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollTo( hasDescendant(withText("not in the list")) )); }
Kotlin
@Test fun scrollToItemBelowFold_checkItsText() { // First, scroll to the position that needs to be matched and click on it. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform( RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition( ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD, click() ) ) // Match the text in an item below the fold and check that it's displayed. val itemElementText = "${activityRule.activity.resources .getString(R.string.item_element_text)} ${ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD.toString()}" onView(withText(itemElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())) }
Java
@Test public void scrollToItemBelowFold_checkItsText() { // First, scroll to the position that needs to be matched and click on it. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition(ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD, click())); // Match the text in an item below the fold and check that it's displayed. String itemElementText = activityRule.getActivity().getResources() .getString(R.string.item_element_text) + String.valueOf(ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD); onView(withText(itemElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())); }
Kotlin
@Test fun itemInMiddleOfList_hasSpecialText() { // First, scroll to the view holder using the isInTheMiddle() matcher. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToHolder(isInTheMiddle())) // Check that the item has the special text. val middleElementText = activityRule.activity.resources .getString(R.string.middle) onView(withText(middleElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())) }
Java
@Test public void itemInMiddleOfList_hasSpecialText() { // First, scroll to the view holder using the isInTheMiddle() matcher. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToHolder(isInTheMiddle())); // Check that the item has the special text. String middleElementText = activityRule.getActivity().getResources() .getString(R.string.middle); onView(withText(middleElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())); }
מקורות מידע נוספים
למידע נוסף על השימוש ברשימות אספרסו בבדיקות Android, אפשר לעיין ב במקורות המידע הבאים.
דוגמיות
- DataAdapterSample:
מציג את נקודת הכניסה
onData()ל-Espresso, לרשימות ול-AdapterViewאובייקטים.

