Espresso には、2 つのユーザーを対象に、特定のアイテムまでスクロールする、または特定のアイテムを操作するメカニズムが備わっています。 アダプター ビューとリサイクラー ビューがあります。
リスト、特に RecyclerView や
AdapterView オブジェクトを使用すると、目的のビューがまだ存在しない可能性があります。
表示されるのは少数の子要素のみであるため、
スクロールするとリサイクルされますこの場合、scrollTo() メソッドは使用できません。
既存のビューが必要であるためです
アダプター ビューのリスト項目の操作
onView() メソッドを使用する代わりに、onData() で検索を開始します。
マッチングするビューのベースとなるデータに対するマッチャーを提供します。
Espresso は、Adapter オブジェクト内の行を見つける作業をすべて行い、
ビューポートにアイテムを表示します
カスタムビュー マッチャーを使用したデータのマッチング
以下のアクティビティには、SimpleAdapter を基盤とする ListView が含まれています。
これは、Map<String, Object> オブジェクトの各行のデータを保持します。
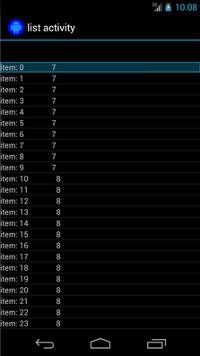
各マップには、2 つのエントリがあります。1 つのキー "STR" で、
"item: x"、鍵 "LEN" は Integer という形式で、
必要があります。例:
{"STR" : "item: 0", "LEN": 7}
「item: 50」の行をクリックするコードは次のようになります。
Kotlin
onData(allOf(`is`(instanceOf(Map::class.java)), hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), `is`("item: 50")))).perform(click())
Java
onData(allOf(is(instanceOf(Map.class)), hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), is("item: 50")))) .perform(click());
なお、Espresso によりリストは必要に応じて自動的にスクロールされます。
onData() 内の Matcher<Object> を細かく見てみましょう。「
is(instanceOf(Map.class)) メソッドを使用すると、検索対象を
AdapterView は、Map オブジェクトを基盤としています。
この例では、クエリのこの側面はリストビューのすべての行に一致しますが、 特定の項目をクリックする必要があるため、次のように検索対象を絞り込みます。
Kotlin
hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), `is`("item: 50"))
Java
hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), is("item: 50"))
この Matcher<String, Object> は、次を含むエントリを含むすべてのマップに一致します。
キー "STR" と値 "item: 50" です。これを検索するコードは
他の場所で再利用したい場合は
そのための withItemContent マッチャー:
Kotlin
return object : BoundedMatcher<Object, Map>(Map::class.java) { override fun matchesSafely(map: Map): Boolean { return hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), itemTextMatcher).matches(map) } override fun describeTo(description: Description) { description.appendText("with item content: ") itemTextMatcher.describeTo(description) } }
Java
return new BoundedMatcher<Object, Map>(Map.class) { @Override public boolean matchesSafely(Map map) { return hasEntry(equalTo("STR"), itemTextMatcher).matches(map); } @Override public void describeTo(Description description) { description.appendText("with item content: "); itemTextMatcher.describeTo(description); } };
タイプのオブジェクトのみを一致させるため、BoundedMatcher をベースとして使用する。
Map。matchesSafely() メソッドをオーバーライドし、見つかったマッチャーを挿入します。
Matcher<String>
渡します。これにより、withItemContent(equalTo("foo")) を呼び出せるようになります。コード
equalTo() を呼び出している別のマッチャーを作成して、
は、String オブジェクトを受け入れます。
Kotlin
fun withItemContent(expectedText: String): Matcher<Object> { checkNotNull(expectedText) return withItemContent(equalTo(expectedText)) }
Java
public static Matcher<Object> withItemContent(String expectedText) { checkNotNull(expectedText); return withItemContent(equalTo(expectedText)); }
これで、項目をクリックするためのコードは次のように簡単になります。
Kotlin
onData(withItemContent("item: 50")).perform(click())
Java
onData(withItemContent("item: 50")).perform(click());
このテストの完全なコードについては、testClickOnItem50() メソッドをご覧ください。
AdapterViewTest
クラスと
このカスタムLongListMatchers
matcher をご覧ください。
特定の子ビューのマッチング
上記のサンプルでは、ListView の行全体の中央でクリックを行います。
今度は、行の特定の子要素を操作する場合を考えてみましょう。たとえば、
LongListActivity の行の 2 列目をクリックしようとしています。
これは、最初の列のコンテンツの String.length を表示します。

onChildView() の仕様を
DataInteraction:
Kotlin
onData(withItemContent("item: 60")) .onChildView(withId(R.id.item_size)) .perform(click())
Java
onData(withItemContent("item: 60")) .onChildView(withId(R.id.item_size)) .perform(click());
リサイクラー ビューのリスト項目の操作
RecyclerView オブジェクトは AdapterView オブジェクトと動作が異なるため、
onData() を使用して操作することはできません。
Espresso を使用して RecyclerView を操作するには、
espresso-contrib パッケージには、次のコレクションが含まれます。
RecyclerViewActions
位置へのスクロールやアイテムに対するアクションを行うために使用できます。
scrollTo()- 一致するビューが存在する場合、そのビューまでスクロールします。scrollToHolder()- 一致するビューホルダーが存在する場合は、そのビューホルダーまでスクロールします。scrollToPosition()- 特定の位置までスクロールします。actionOnHolderItem()- 一致するビューホルダーに対してビュー アクションを実行します。actionOnItem()- 一致するビューに対してビュー アクションを実行します。actionOnItemAtPosition()- 特定の位置でビューに対してビュー アクションを実行します。
次のスニペットは、 RecyclerViewSample サンプル:
Kotlin
@Test(expected = PerformException::class) fun itemWithText_doesNotExist() { // Attempt to scroll to an item that contains the special text. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform( // scrollTo will fail the test if no item matches. RecyclerViewActions.scrollTo( hasDescendant(withText("not in the list")) ) ) }
Java
@Test(expected = PerformException.class) public void itemWithText_doesNotExist() { // Attempt to scroll to an item that contains the special text. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) // scrollTo will fail the test if no item matches. .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollTo( hasDescendant(withText("not in the list")) )); }
Kotlin
@Test fun scrollToItemBelowFold_checkItsText() { // First, scroll to the position that needs to be matched and click on it. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform( RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition( ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD, click() ) ) // Match the text in an item below the fold and check that it's displayed. val itemElementText = "${activityRule.activity.resources .getString(R.string.item_element_text)} ${ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD.toString()}" onView(withText(itemElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())) }
Java
@Test public void scrollToItemBelowFold_checkItsText() { // First, scroll to the position that needs to be matched and click on it. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition(ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD, click())); // Match the text in an item below the fold and check that it's displayed. String itemElementText = activityRule.getActivity().getResources() .getString(R.string.item_element_text) + String.valueOf(ITEM_BELOW_THE_FOLD); onView(withText(itemElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())); }
Kotlin
@Test fun itemInMiddleOfList_hasSpecialText() { // First, scroll to the view holder using the isInTheMiddle() matcher. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToHolder(isInTheMiddle())) // Check that the item has the special text. val middleElementText = activityRule.activity.resources .getString(R.string.middle) onView(withText(middleElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())) }
Java
@Test public void itemInMiddleOfList_hasSpecialText() { // First, scroll to the view holder using the isInTheMiddle() matcher. onView(ViewMatchers.withId(R.id.recyclerView)) .perform(RecyclerViewActions.scrollToHolder(isInTheMiddle())); // Check that the item has the special text. String middleElementText = activityRule.getActivity().getResources() .getString(R.string.middle); onView(withText(middleElementText)).check(matches(isDisplayed())); }
参考情報
Android テストで Espresso リストを使用する方法の詳細については、 ご覧ください
サンプル
- DataAdapterSample:
Espresso の
onData()エントリ ポイント(リストとAdapterView)を示します。 説明します。

