รายการช่วยให้ผู้ใช้เลือกรายการจากชุดตัวเลือกต่างๆ ได้อย่างง่ายดายในอุปกรณ์ Wear OS
ไลบรารี UI ของอุปกรณ์ที่สวมใส่ได้ประกอบด้วยคลาส
WearableRecyclerView ซึ่งเป็นการใช้งานRecyclerViewเพื่อสร้างรายการที่เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพสำหรับอุปกรณ์ที่สวมใส่ได้ คุณใช้อินเทอร์เฟซนี้ในแอปที่สวมใส่ได้โดยใช้การสร้างคอนเทนเนอร์ WearableRecyclerView ใหม่
ใช้ WearableRecyclerView สำหรับรายการแบบยาวที่มีรายการง่ายๆ เช่น ตัวเปิดแอปพลิเคชันหรือรายชื่อติดต่อ แต่ละรายการอาจมีสตริงสั้นๆ และไอคอนที่เชื่อมโยง หรือแต่ละรายการอาจมีเพียงสตริงหรือไอคอน
หมายเหตุ: หลีกเลี่ยงเลย์เอาต์ที่ซับซ้อน ผู้ใช้ควรเห็นไอเทมเพียงแวบเดียวก็เข้าใจได้ว่าเป็นไอเทมอะไร โดยเฉพาะเมื่อใช้กับอุปกรณ์ที่สวมใส่ได้ซึ่งมีหน้าจอขนาดเล็ก
การขยายคลาส RecyclerView ที่มีอยู่ทำให้ WearableRecyclerView
API แสดงรายการรายการที่เลื่อนในแนวตั้งในรายการแนวตรงโดยค่าเริ่มต้น นอกจากนี้ คุณยังใช้ WearableRecyclerView API เพื่อเลือกใช้เลย์เอาต์แบบโค้งและท่าทางสัมผัสแบบวงกลมในแอปอุปกรณ์ที่สวมใส่ได้ด้วย

รูปที่ 1 มุมมองรายการเริ่มต้นใน Wear OS
คู่มือนี้จะแสดงวิธีใช้คลาส WearableRecyclerView เพื่อสร้างรายการในแอป Wear OS, วิธีเลือกใช้เลย์เอาต์โค้งสำหรับรายการที่เลื่อนได้ และวิธีปรับแต่งลักษณะที่ปรากฏของรายการย่อยขณะเลื่อน
เพิ่ม WearableRecyclerView ลงในกิจกรรมโดยใช้ XML
เลย์เอาต์ต่อไปนี้จะเพิ่ม WearableRecyclerView ลงในกิจกรรม
<androidx.wear.widget.WearableRecyclerView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/recycler_launcher_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:scrollbars="vertical" />
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดง WearableRecyclerView
ที่ใช้กับกิจกรรม
Kotlin
class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) } ... }
Java
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); } ... }
สร้างเลย์เอาต์แบบโค้ง
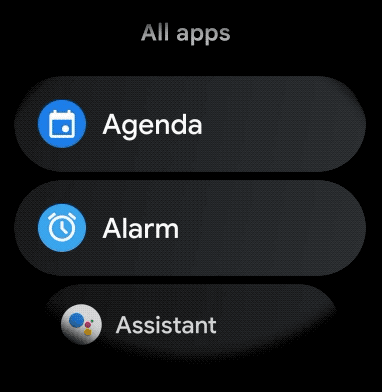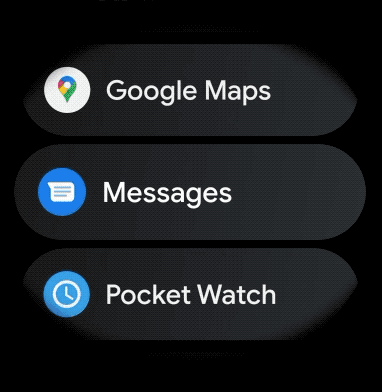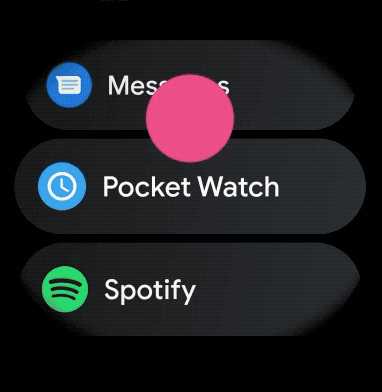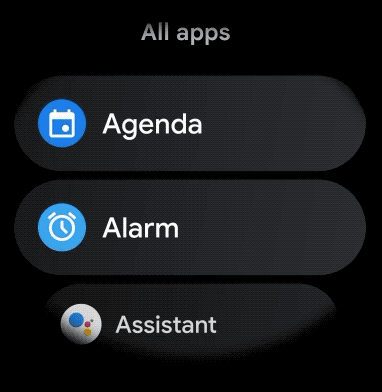
หากต้องการสร้างเลย์เอาต์โค้งสำหรับรายการที่เลื่อนได้ในแอปสำหรับอุปกรณ์สวมใส่ ให้ทำดังนี้
-
ใช้
WearableRecyclerViewเป็นคอนเทนเนอร์หลักในเลย์เอาต์ XML ที่เกี่ยวข้อง -
ตั้งค่าวิธีการ
setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(boolean)เป็นtrueซึ่งจะจัดรายการแรกและรายการสุดท้ายในรายการให้อยู่กึ่งกลางในแนวตั้งบนหน้าจอ -
ใช้เมธอด
WearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager()เพื่อกำหนดเลย์เอาต์ของรายการบนหน้าจอ
Kotlin
wearableRecyclerView.apply { // To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. isEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled = true ... layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this@MainActivity) }
Java
// To align the edge children (first and last) with the center of the screen. wearableRecyclerView.setEdgeItemsCenteringEnabled(true); ... wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this));
หากแอปมีข้อกำหนดเฉพาะในการปรับแต่งลักษณะที่ปรากฏของรายการย่อยขณะเลื่อน เช่น การปรับขนาดไอคอนและข้อความขณะที่รายการเลื่อนออกจากตรงกลาง ให้ขยายคลาส
WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback และลบล้างเมธอด
onLayoutFinished
ข้อมูลโค้ดต่อไปนี้แสดงตัวอย่างการปรับแต่งการเลื่อนของรายการเพื่อปรับขนาดให้ห่างจากตรงกลางมากขึ้นด้วยการเพิ่มคลาส WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback
Kotlin
/** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private const val MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback : WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback() { private var progressToCenter: Float = 0f override fun onLayoutFinished(child: View, parent: RecyclerView) { child.apply { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. val centerOffset = height.toFloat() / 2.0f / parent.height.toFloat() val yRelativeToCenterOffset = y / parent.height + centerOffset // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset) // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS) scaleX = 1 - progressToCenter scaleY = 1 - progressToCenter } } }
Java
public class CustomScrollingLayoutCallback extends WearableLinearLayoutManager.LayoutCallback { /** How much icons should scale, at most. */ private static final float MAX_ICON_PROGRESS = 0.65f; private float progressToCenter; @Override public void onLayoutFinished(View child, RecyclerView parent) { // Figure out % progress from top to bottom. float centerOffset = ((float) child.getHeight() / 2.0f) / (float) parent.getHeight(); float yRelativeToCenterOffset = (child.getY() / parent.getHeight()) + centerOffset; // Normalize for center. progressToCenter = Math.abs(0.5f - yRelativeToCenterOffset); // Adjust to the maximum scale. progressToCenter = Math.min(progressToCenter, MAX_ICON_PROGRESS); child.setScaleX(1 - progressToCenter); child.setScaleY(1 - progressToCenter); } }
Kotlin
wearableRecyclerView.layoutManager = WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, CustomScrollingLayoutCallback())
Java
CustomScrollingLayoutCallback customScrollingLayoutCallback = new CustomScrollingLayoutCallback(); wearableRecyclerView.setLayoutManager( new WearableLinearLayoutManager(this, customScrollingLayoutCallback));


